A new method for seismic noise removal based on deep learning consistently produces superior results to traditional noise attenuation processes. The fully automated noise attenuation method has been developed that eliminates the need for time-consuming and subjective user parameter testing.

Both instrumental and environmental noise needs to be removed from motion sensor records in multisensor streamer acquisition. The new method is outlined in a PGS First Break paper in February and consists of two convolutional neural network models. The first model attenuates vertical narrow band high amplitude noise mainly generated by the instruments attached to the streamers such as eBirds. While the second model attenuates widespread background noise mainly associated with environmental conditions such as waves and currents.
Read the full paper 'Motion sensor noise attenuation using deep learning'
The models were trained using motion sensor data recorded in the field with supervised learning where the desired outputs were produced by alternative workflows.
The workflow has been extensively validated using records from different surveys acquired in different parts of the world. Throughout the validation process, there was no need for any workflow modification, the workflow is automated and does not require any user interaction. The parameter testing phase that is needed for conventional noise attenuation approaches has been eliminated.
Compared to many other convolutional neural network architectures used for seismic noise attenuation, our final architecture has fewer parameters and, therefore, uses fewer hardware resources. The workflow has been recently used for several full survey productions.
The new workflow can attenuate more noise from the motion sensor records than what could be achieved with previous workflows, and at the same time, it has better signal preservation without any user interaction.
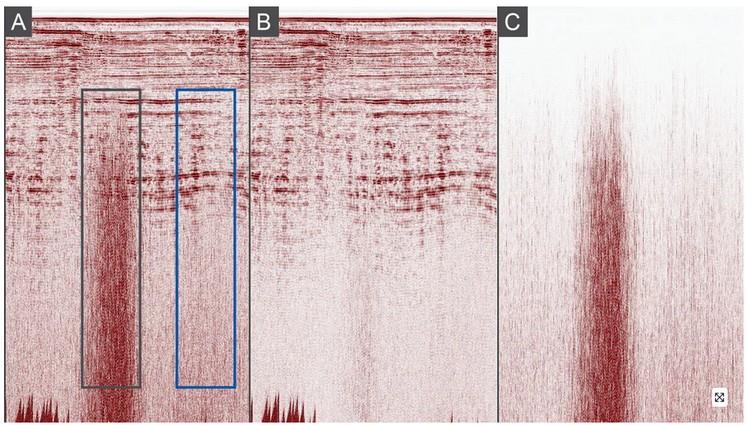
Motion sensor 2D QC stack from the Outer Moray Firth A: input, B: output and C: attenuated energies using the proposed noise attenuation workflow. The black box shows the dominant environmental noise and blue box shows dominant instrument noise.
Source: PGS











