For the first time, a new scientific publication has documented a young source rock with widespread presence in the Norwegian Sea.
The presence of a source rocks is the number one prerequisite for forming petroleum. Documentation of a new source rock can create new exploration opportunities, particularly in areas with no previously known source rocks.
The Norwegian Offshore Directorate has been involved in studies of natural oil seeps on the NCS over several years. These studies have yielded new knowledge about a young source rock that, so far, has been overlooked.

Published on ScienceDirect
In a new article on the online research platform ScienceDirect, much of the work is compiled and documented scientifically.
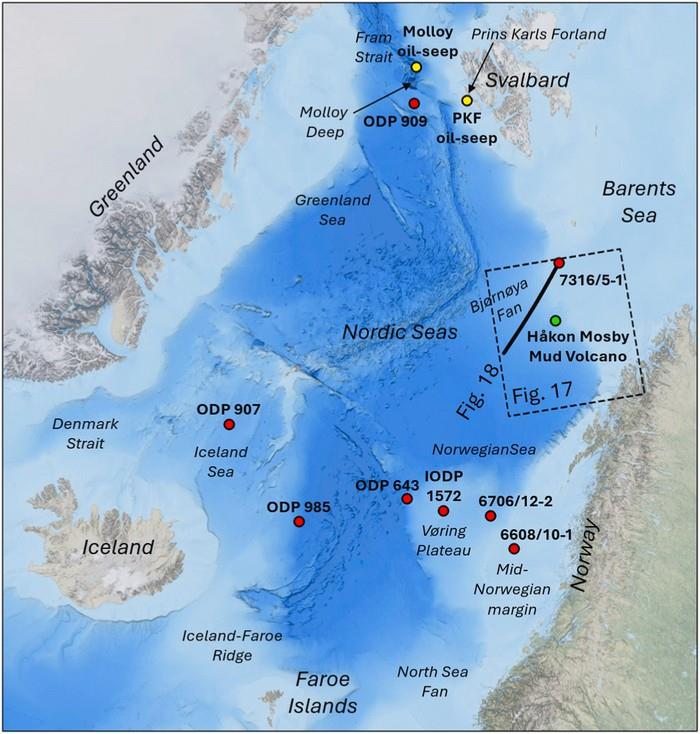
This publication links natural oil seeps west of Svalbard with proven Early to Middle Miocene (in this context, about 17 million years ago) intervals in several scientific boreholes and exploration wells in large parts of the Norwegian Sea (see map below).
Too shallow?
Basin modelling shows that this source rock can be oil-mature below the Bjørnøya Fan west of the Barents Sea.
'One of the most exciting results is that the studies document a young source rock from what used to be a large-scale deltaic sedimentary environment in large parts of the Norwegian Sea. The sedimentary conditions can best be compared with the conditions in the Niger and Congo deltas off the coast of West Africa'.
Those were the words of geologist Rune Mattingsdal at the Norwegian Offshore Directorate, who is a co-author of the publication.
Despite the fact that, in most places, the source rock will most likely be buried too shallow to form oil, it may, as is the case below the Bjørnøya Fan, potentially be buried deep enough to form hydrocarbons in several locations in existing APA acreage (APA, awards in pre-defined areas) in the Norwegian Sea, in areas that have not yet been explored with regard to this opportunity.
Source: Norwegian Offshore Directorae